|
A storage controller manages the flow of information between the server and the data, assigning two paths, in case one of the paths fails or is overloaded. For the best levels of performance and availability, every layer of technology must be balanced.
Comparing the throughput of your controllers
| 1. | Log on to the BMC ProactiveNet Operations Console. |
| 2. | Display the list of devices monitored by BPPM: |
| • | In the Navigation frame, select the Main drawer. |
| • | Click  to display the list of devices in a grid. to display the list of devices in a grid. |
| 3. | Click the subsystem of the controllers you need to compare the distribution workload. |
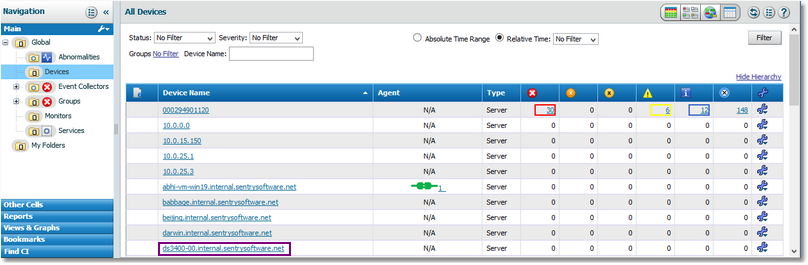
Selecting a Device
| 4. | The list of monitors for your device is displayed. Select the first of the two controllers for which you need to compare throughput. |
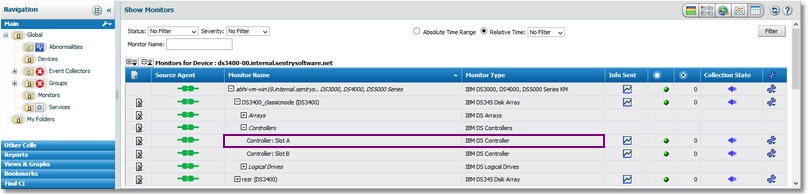
Displaying the Monitors
| 5. | Click  for the chosen disk array. for the chosen disk array. |
| 6. | By default, the Request Rate and Transfer Byte Rate attributes are displayed. You will need to modify the attributes selection to display the ones you need: |
| • | Click the Attributes & Indicators tab. |
| • | Deselect the Request Rate attribute and keep the Transfer Byte Rate attribute checked. |
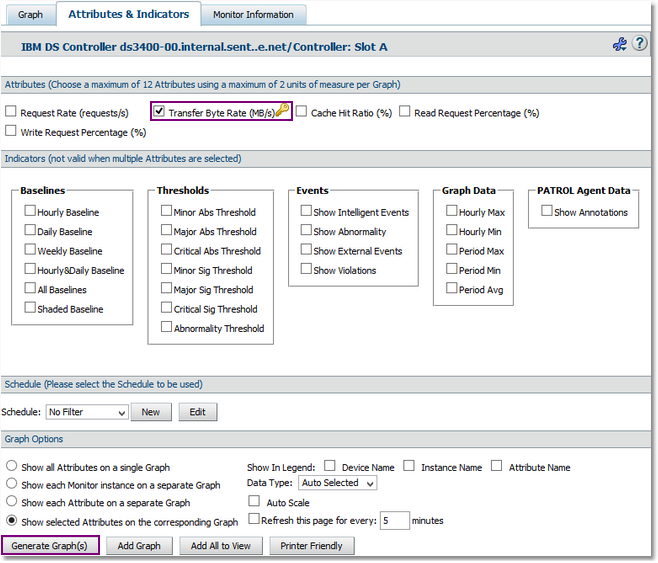
Selecting the Attributes to Display in the Graph
| 7. | Add the graph to the view: |
| • | Click  . The following pop-up is displayed: . The following pop-up is displayed: |
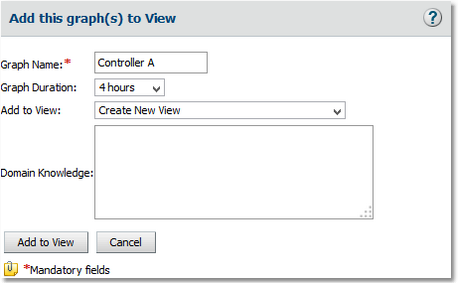
Adding a Graph to View - Step 1
Adding a Graph to View - Step 2
| • | In the View Title field, type Controllers Workload Balance and click Add View. The View created successfully message appears. Click Close. |
| 8. | The Controllers Workload Balance view is now created and available under the Views & Graphs drawer in the Navigation pane. |
| 9. | Create a graph for the second controller and add it to the Controllers Workload Balance view. You are then able to easily compare the values of both controllers to evaluate the workload distribution. |
For example, if the throughput on one controller is significantly higher than the other one, it indicates that one on the controllers may constitute a bottleneck for the subsystem that could be alleviated by better sharing the load between the controllers.
It is recommended to pay close attention to which logical drive is handled by which controller, depending on the activity of this logical drives to be able to reallocates controller to drive I/O activity so that neither controller is overloaded.
| 




