-
Home
- Troubleshooting
Hardware Sentry CLI (hws)
Overview
The hws CLI is the core Hardware Sentry engine wrapped in a command line interface. System administrators can easily invoke this tool in a shell to discover the hardware components of the specified host and report any hardware-related problem.
Discovered components include:
- Enclosure (manufacturer, model, serial number)
- Processors
- Memory modules
- GPUs
- Disks (HDD, SDD, RAID)
- Network and Fiber Channel Adapters
- Sensors (temperature, voltage, fans, power, LEDs)
Supported systems include:
- Servers (Linux, AIX, HP-UX, Solaris, Windows, in-band and out-of-band)
- Blade chassis
- Network switches
- SAN switches
- Storage systems (disk arrays, filers, tape libraries)
The detailed list of supported systems (manufacturer and product family and the required instrumentation stack) is listed in Sentry's Hardware Connectors Library.
The quantity and quality of the information that Hardware Sentry will gather depends on the instrumentation stack available on the targeted host.
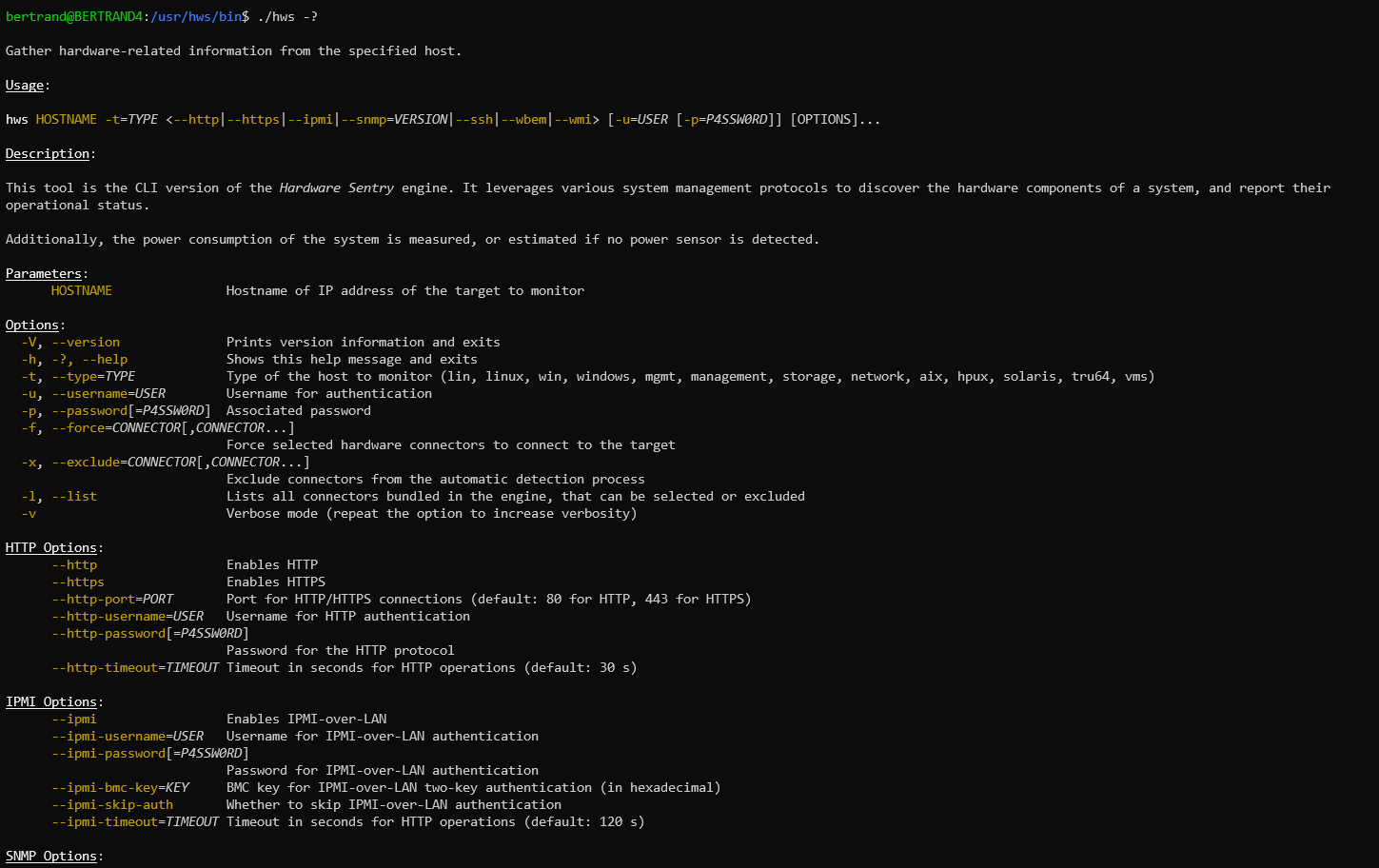
Only a few options are required to run the hws command:
- Hostname or IP address of the device to be monitored
- Device type
- Protocols to be used:
- HTTP
- IPMI-over-LAN
- SSH
- SNMP
- WBEM
- WMI (on Windows only)
- Credentials
The hws command can be used to troubleshoot the monitoring performed by the Hardware Sentry Agent (the core engine) or by other Hardware Sentry products such as the KM for PATROL.
The Basics
The hws command invokes the Hardware Sentry Engine against one host and performs 3 tasks:
- Detection of the instrumentation stack on the targeted host
- Discovery of the hardware components
- Collection of metrics and status for each hardware component
The hws command requires a few parameters to run:
- the hostname to connect to
- the type of the host (Windows, Linux, Management, Storage, Network, AIX, HP-UX, Solaris)
- the protocols to use to gather information from the host (HTTP, IPMI, SNMP, SSH, WBEM or WMI)
- the credentials
Example:
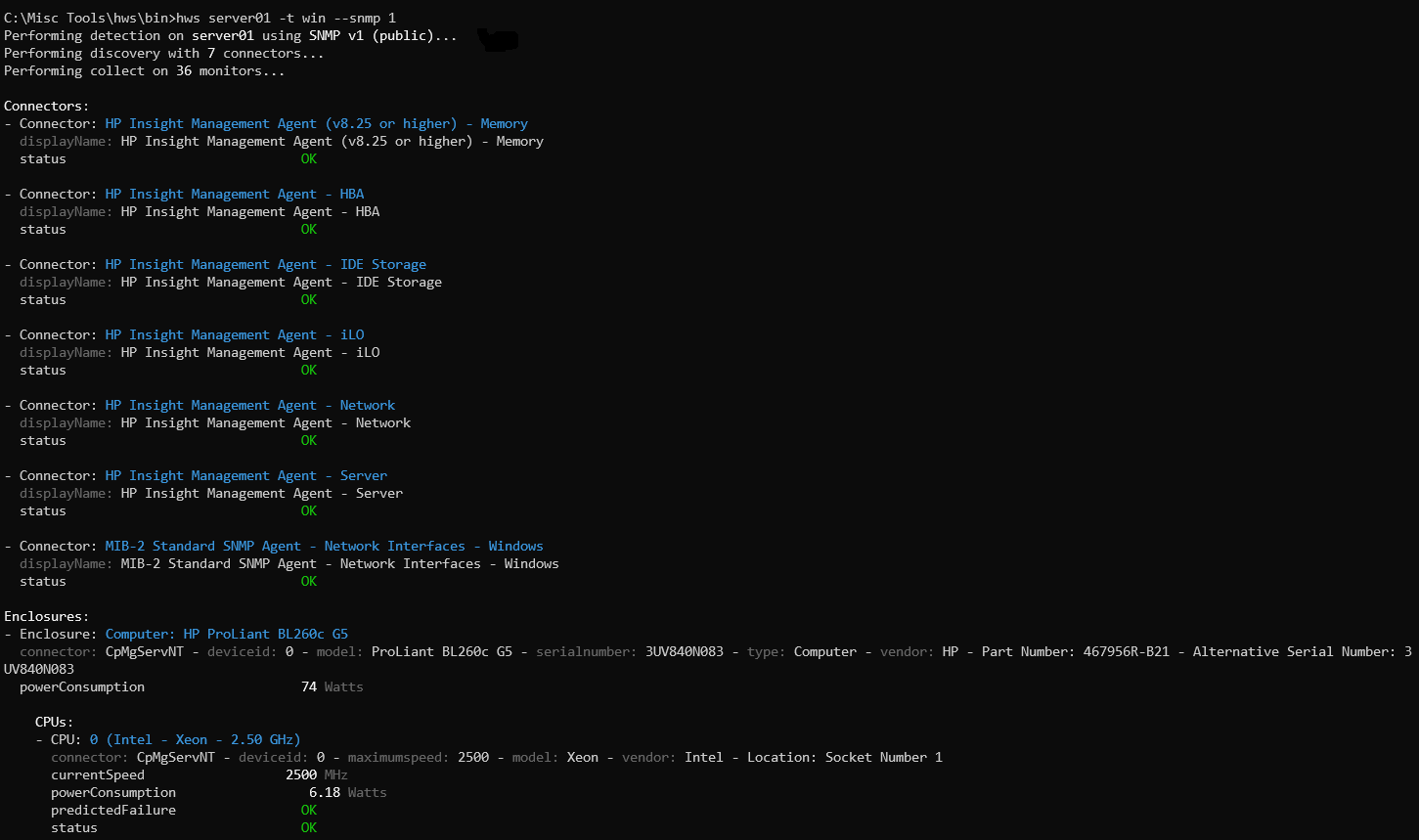
$ hws server01 -t win --snmp 1 --community secret
The above command will connect to server01 (a Windows system), and will detect which instrumentation stack responds to SNMP version 1 with the secret community.
Assuming server01 is an HP ProLiant server with the HP Insight Management Agent, the hws output will look like:

To learn more about the various options available, simply run the below command:
$ hws -h
Verbose Modes
To get additional details about the operations performed by the Hardware Sentry Engine, run:
-vto display internal warning messages (WARN)-vvto get details about each operation performed (INFO)-vvvto get initialization and connections details (DEBUG)-vvvvto get full visibility about what is happening (TRACE)
Examples
Storage System, REST API
$ hws STOR01 -t storage --https -u USER
This command will connect to the STOR01 storage system in HTTPS (port 443 by default) and check whether a known REST API responds with the USER credentials. The password will be asked for interactively. Use the -p P4SSW0RD option to specify the password directly in the command line (not secure!).
Linux, SNMP v1
$ hws HOST02 -t linux --snmp 1 --community COMM02
This command will connect to the HOST02 Linux system using SNMP version 1 and the COMM02 community. If a known SNMP agent is running on this host, hws will leverage it to discover the physical components of the system and collect various metrics.
Note: If no SNMP community is specified, public is assumed by default.
Storage System, SNMP v3
$ hws CISC03 -t sto --snmp 3-sha -u USER --snmp-privacy AES --snmp-privacy-password MYSECRET
This command will connect to the CISC03 SAN switch (storage) using SNMP version 3 using SHA-based authentication as USER. Communication will be encrypted using AES with the MYSECRET privacy password.
Note: SAN switches fall into the Storage category of systems, like disk arrays and tape libraries, and not in the
Networkcategory, like network switches and IP routers.
Windows, WMI and SNMP v2c
C:\Program Files\hws> hws WIN04 -t win --snmp 2 --wmi
This command will connect to the WIN04 Windows system using SNMP version 2c with the public (default) community, and WMI as the current.
Note: The WMI protocol can only be used from a Windows system to monitor another Windows system.
Windows, WMI and SNMP v3 (Alternate Credentials)
C:\Program Files\hws> hws WIN05 -t win --snmp 3-sha --snmp-username USERA --wmi --wmi-username WINUSER
This command will connect to the WIN05 Windows system using SNMP version 3 as USERA, and WMI as WINUSER. Both passwords will be asked for interactively.
Note: Instead of using the common
-uor--usernameoptions, we had to use the--snmp-usernameand--wmi-usernameoptions to specify different credentials for SNMP and WMI.
Ouf-of-band Management Card, IPMI-over-LAN
$ hws MGMT06 -t oob --ipmi -u USER
This command will connect to the MGMT06 out-of-band management card (typically a BMC chip) using the IPMI-over-LAN protocol as USER.
VMware ESX, WBEM
$ hws ESX07 -t esx --wbem -u admin
This command will connect to the ESX07 VMware ESX host using the WBEM protocol (HTTPS/5989 by default) with the admin account.
VMware vCenter, WBEM
$ hws ESX08 -t esx --wbem -u admin --wbem-vcenter=vcenter01
This command uses the multi-tier authentication vcenter01 server, which provides a connection ticket to access the ESX08 VMware ESX host via the WBEM protocol (HTTPS/5989 by default) with the admin account.
Solaris, SSH
$ hws SOLAR08 -t sol --ssh -u USER --sudo-command-list /usr/sbin/dladm,/usr/sbin/ndd
This command will connect to the SOLAR08 Solaris system using the SSH protocol to execute commands as USER. sudo will be used to execute the /usr/sbin/dladm and /usr/sbin/ndd commands, as they require root privileges.
Note: The system must have been configured to allow
USERto execute these commands withsudo.
WinRM
$ hws WIN09 -t mgmt --winrm --winrm-username USER --winrm-password MYSECRET
This command will connect to the WIN09 system using the WinRM protocol to execute commands as USER.
Automatic Detection vs Manual Selection
Hardware Sentry is bundled with Sentry's Hardware Connector Library, a library which consists of hundreds of hardware connectors that describe how to discover hardware components and detect failures in a given system, with a specific instrumentation stack.
Examples of connectors:
- Dell OpenManage Server Administrator (SNMP)
- Network Cards on Windows (WMI)
- IBM AIX physical disks, using system commands
- VMware ESX (WBEM)
- etc.
When running the hws command, the connectors are automatically selected based on the specified system type and the protocol enabled. This is the detection phase.
You can however specify manually which connectors must be used to monitor the specified host, or exclude some connnectors from the list that will be tested during the detection phase.
Force Connectors
To force specific connectors to be used, add the --force CONNECTOR,... option, where CONNECTOR,... is a comma-separated list of connector internal names (you need to use their id).
Using the --force option will shorten the detection phase, as only the specified connectors will be tested.
To get the list of connectors bundled in Hardware Sentry and their corresponding internal name (id), you can run the below command:
$ hws --list
This will provide a list as below:
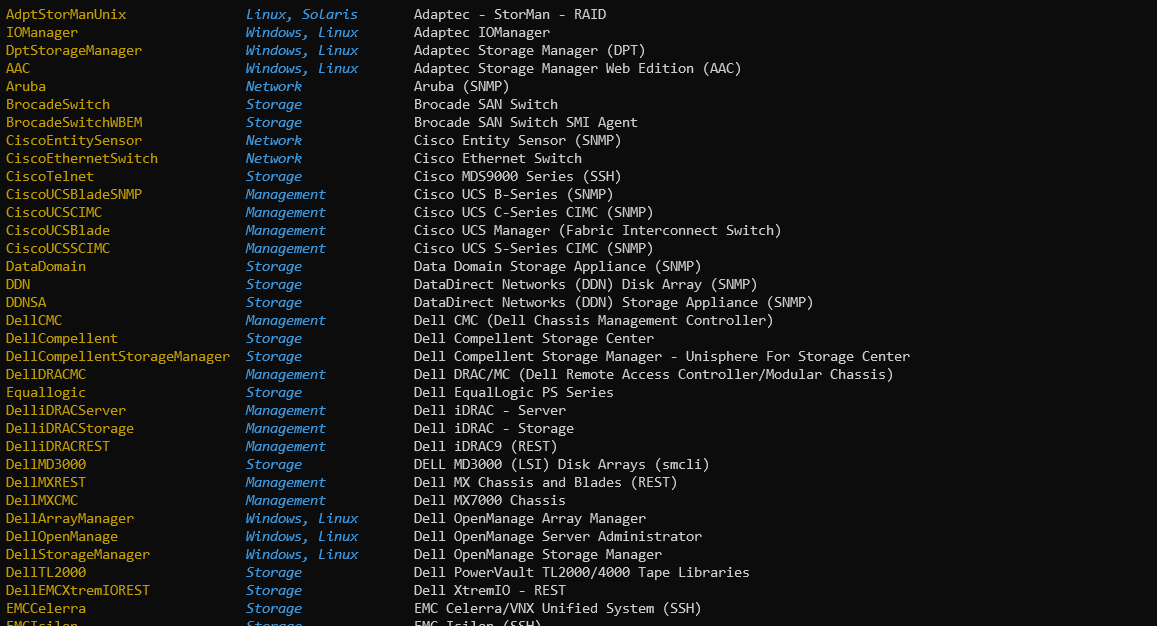
This list displays the internal name (id) of each connector, its applicable system types (to use with the --type option) and its display name. You need to use the connector's internal name (id) in the --force option.
Exclude Connectors
To exclude specific connectors from being tested in the detection phase, use the --exclude CONNECTOR,... option, where CONNECTOR,... is a comma-separated list connectors' internal name (id).
Sequential Mode
By default, the Hardware Sentry Engine sends the queries simultaneously to the host. Although the parallel transmission is faster than the sequential one, too many requests at the same time can lead to the failure of the targeted host.
Use the --sequential option to force all the requests to be executed in a sequential order, thus the monitored host is not overloaded.
$ hws SERVER01 -t linux --snmp 1 --community COMM02 --sequential